Dictionary
AC refers to alternating current electricity. 110 volts AC is the type of electricity most often found in home and office electrical outlets in the United States. Outside the U.S. many countries have standard outlet voltage of 220 ~ 240 volts AC. In addition, many CCTV products use 24 volts AC, for which a separate power transformer is required.
AC/DC refers to changing between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC). Switching from AC power from your home or office outlet to DC current is required for most of our products. A transformer can easily be used to regulate the current; for this reason, we include AC/DC power supplies with almost all of our products. There are also power inverters which convert DC current to AC current. Such power inverters are commonly used to power 110 volt AC devices (such as a VCR video recorder) from a DC automotive or marine battery.
Alarm/Event Operation is a feature found in many CCTV video recording devices like VCRs and DVRs. This allows the user to interface alarm sensors (like a PIR motion detector) with the recording device through an alarm in/out port (this port has a physical electrical contact). An alarm/event capable recorder can then be set to automatically start and stop recording when the alarm is triggered (such as by motion). However, the digital revolution is replacing the need for bulky and expensive alarm sensors. Many newer digital DVR recorders feature advanced video motion detection, which can provide dynamic motion detection recording with built-in software alone.
Alarm Input Some cameras and video servers have the ability to accept alarm inputs. These are inputs from standard sensor devices such as, Passive Infra-red (PIR) detectors, door contacts, active beams etc. or relay outputs from intruder alarm panels, or access control panels. Alarm input circuits can come in a number of forms. Most commonly they are self powered, so will operate with a passive switch style circuit. However, in some cases, they expect to be provided with power (normally 12V) as the signal of open or closed. In a few cases manufactures only supply TTL (very low voltage) level inputs. In that case, they can only be safely used with normal alarm sensors in conjunction with some additional isolation circuitry. In this case, it is best to contact the manufacturer for advice.
Alkaline Battery - This is a type of battery most commonly found at retailers around the world. Alkaline batteries are suggested to power all video equipment using the mobile BAT-1, BAT-3, or BAT-AAA battery packs. For some products (those with input voltage as low as 9.6 volts DC), however, rechargeable Nickel-Metal-Hydride batteries may also be used. In addition, using lead acid, lithium-ion, or lithium polymer batteries may also provide adequate power for video cameras and other devices so long as the +/- polarity is correct and the batterys output voltage falls within the devices safe operating range.
Amps (A) are used to measure electrical current consumption. 1 amp (A) = 1000 milliamps (mA).
Amplifier typically refers to a device which adds strength to a signal for a better and / or longer performance ability. Amplifiers can be found for both wired and wireless equipment. A VDA (video distribution amplifier) is designed to extend a video signal through wires by boosting the power of the video signal. Transmitter-end and receiver-end amplifiers can be found for wireless equipment to help increase broadcast range potential.
Analogue Continuously variable numerical values such as voltage, current, etc. (The CCD camera produces analogue video signals.)
Angle of View the scene angle that a video camera lens can show on the monitor, like Diagonal Angle, Horizontal Angle and Vertical Angle, usually described in degree.
Antenna Element - Antennas for wireless equipment are constructed of elements which are specifically tuned to a given frequency or range of frequency to improve gain.
Antenna Gain refers to any increase or decrease in the strength of a wireless RF radio frequency signal when considering external antenna equipment. Gain is typically measured in terms of decibels (dB) or a number of times of magnification.
Antenna Type refers to the design of a particular antenna. Common antenna types for wireless CCTV are dipole whip antenna (the most common), yagi, flat panel, omni-directional, parabolic dish, and heliophase.
Aperture The light gathering area of a lens, controlled by the iris.
ARP Address Resolution Protocol; for mapping an IP address to a physical machine address.
Aspherical Lens A lens designed with a non spherical shape so that it passes more lights or decreases barrel distortion on wide angle lenses.
Aspect Ratio is a specification for monitors. This term refers to the ratio between the width and height of a video image. Typically, CCTV cameras produce an aspect ratio of 4:3 (the vertical size of the picture is 75% of the horizontal width). This is the same ratio for compatibility with standard consumer televisions and video equipment as well as security-industry monitors and video recorders. Widescreen televisions, on the other hand, have a 16:9 aspect ratio. Attenuation A decrease or loss in a signal, usually measured in decibels.
Audio indicates sound. When audio is listed as a feature of some video product, this usually means one of a few things: a device for monitoring sound (microphone), a wireless transmitters ability to broadcast sound, or a video recorders ability to record audio.
Audio Input Plug refers to the type of connector plug for a devices audio input jack. In most cases, this is a standard RCA connector or 1/8" (3.5mm) mini plug.
Audio Input Type - There are two basic kinds of audio found for video equipment connections: line-level and mic-level. Line-level indicates that the audio input device (like a microphone) must be preamplified in order to record or broadcast the audio signal. All wireless products, recorders, and monitors require line-level microphone connections. For compatibilitys sake, all microphones found on this site are line-level and contain preamplifiers.
Auto electronic shutter (AES) Feature of a camera to adjust for light changes without the use of an auto-iris lens.
Audio Output Plug refers to the type of connector plug for a devices audio output. In most cases, this is a standard RCA connector or 1/8" (3.5mm) mini plug.
Audio Output Type - Audio output for a device can be either line-level or mic-level (see note above in audio input type). So long as the audio output is line-level, there is no need for mic-level connections. Video recorders and monitors typically have line-level inputs, making connections simple.
Auto Iris (AI) Cameras with an Auto Iris feature, have the ability to compensate for large variations in light levels. Particularly useful for cameras that need to compensate for changes from bright sunlight to dark shadows. The auto iris circuitry is normally linked to a motorised iris drive that physically opens and shuts the iris on the lens. Closing a physical iris is a much better way to protect a camera from being damaged by bright sunlight then simply using electronics to reduce the signal strength. A diaphragm device in the lens that adjusts to light level changes. The iris diaphragm opens or closes the aperture to control the amount of lights coming through the lens.
Auto-focus Lens automatically adjusts the lens focus from surrounding scene and keeps a moving object in focus.
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) refers to a circuit within the camera which regulates image brightness levels for optimum performance and highest video quality. This is a feature of many CCTV cameras that helps keep the strength of the output signal constant, even when the light level changes. In other words, it boosts the signal strength at low light levels, and caps it at higher levels.
Auto Homing An automatic sequential video switcher which has manual switches or buttons, which allow a single CCTV camera to be displayed on screen without sequential switching.
Automatic Level Control (ALC) Allows the auto-iris circuitry to either take bright spots more into consideration (peak), bringing out detail in bright areas, or less into consideration (average) bringing out detail in shadows.
Automatic Light Control (ALC) is a built-in feature of every camera found on Eyespyvideo.com. ALC indicates the image sensors ability to automatically adjust in diverse lighting conditions to yield the most vivid video image possible.
Auto-Iris Lens is a lens with a built-in method of automatically controlling the lens aperture for the best video quality under diverse and changing lighting conditions. Auto-iris lenses can be especially helpful under very low light and bright direct forward light. In order to use an auto-iris lens, however, the video camera you are using must have a built-in auto-iris port to supply the lens with a small amount of DC electrical voltage. Manual iris lenses are also available and do not require any special ports or cable connections.
Auto Terminating Automatically select the correct termination depending on whether the video output is connected.
Back Focus is the alignment of the rear of the lens to the imaging device.
Back Light Compensation is a feature of cameras that automatically adjusts the image to compensate for bright sunlight or bright lights, to give more detail on the darker areas of the image. For example to focus on the detail of a face of a person that has the sunlight shining from behind. BLC indicates the image sensors ability to automatically adjust in conditions where lighting is from behind the camera to deliver the sharpest and highest quality video image possible.
Balanced Signal is a method of transmitting audio or video signals over a pair of wires, often twisted pair cable. By sending two equal, but opposite signals, this system minimises external interference, and maintains signal quality.
Balun stands for Balanced - Unbalanced. It is a device used to interface between balanced lines and unbalanced lines. For example, twisted pair to co-axial.
Bandwidth indicates the complete range of frequencies over which a circuit or electronic system can function with minimal signal loss. In effect, bandwidth indicates the amount of information and its complexity which can be carried over a signal. More complex information requires more bandwidth for an effpixels signal. (i.e. color video bandwidth > monochrome video bandwidth > bandwidth for one channel of audio). The capacity of the transmission medium stated in bits per second or as a frequency. Or, the amount of data that can be transmitted in a fixed amount of time. For digital devices, the bandwidth is usually expressed in bits per second (bps) or bytes per second. For analogue devices, the bandwidth is expressed in cycles per second, or Hertz (Hz).
Battery refers to a stored power device. For mobile and remote applications, one or more batteries can be used.
Battery Run Time indicates the amount of time a piece of electronic equipment can realistically be powered using a particular battery pack. For instance, the CC-1HAD color board camera has a battery run time of about 24 hours when using eight fresh "AA" alkaline batteries in our BAT-1 or BAT-3 battery packs. More battery time could potentially be obtained with a higher capacity battery. It must also be noted that the more power consumption load on a battery or battery pack.
Baud A unit of measurement that denotes the number of bits that can be transmitted per second. For example, if a modem is rated at 9600 baud it is capable of transmitting data at a rate of 9600 bits per second.
Bit Abbreviated with small "b". Binary Digit. The smallest unit of data in a computer.
Black & White (monochrome) Camera - Cameras are available with either color or monochrome image sensors. Monochrome cameras are typically referred to as black and white because video image they produce is in shades of gray. Only black and white CCD cameras have the ability to utilize IR infrared lighting. Also, even without infrared lighting, a monochrome camera will generally perform better in low light conditions than will a color camera equipped with a comparable CCD imager, lens, and quality of manufacture. The black and white cameras deliver amazingly crisp video, and in fact much better than the human eye when only a tiny amount of light is available.
Blanking the process whereby the beam in a CRT is cut off during the retrace period.
Blooming The defocusing of regions of the picture where the brightness is at an excessive level, due to enlargement of spot size and halation of the fluorescent screen of the CCTV monitor
BNC Bayonet Neil-Concelman or British Naval Connector BNC is the type of connector plug commonly found on CCTV devices for video and audio input / output connections. BNC is the choice for broadcast video and security video professionals because of its locking design. BNC plugs are easily adapted to standard consumer RCA connectors using a simple one-piece plug adapter. Nearly all products include the necessary adapters so that users can select either BNC or RCA connections to suit their individual requirements for immediate plug and play use. A connector widely used in the CCTV industry, usually for coaxial cable. Easy to install and reliable with little video signal loss.
Bps Bits per Second is the unit used for measuring line speed, the number of information units transmitted per second.
Brightness Control The manual bias control on a cathode ray tube or other display device that controls the average brightness and the contrast of a picture. Brightness Control is a feature found on many monitors. It allows the user to manually select the level of screen backlighting (brightness).
Bridging term used to describe a type of automatic sequential switcher which has the ability to send a signal to two monitors (dual output) - one continually sequencing and the second one able to display any one of the CCTV camera inputs on the "bridged" monitor.
Bullet Camera - A bullet design refers to a camera with a cylindrical shape using an inline video imaging chip (rather than a board design). These cameras are sometimes also called "lipstick cameras" or "inline CCD cameras."
Burned-In Image An image which persists in a fixed position in the output signal of a CCTV camera tube after the camera has been turned to a different scene or, on a CCTV monitor screen.
Byte Abbreviated with capital "B". A unit of data that is eight bits long and is used by most computers to represent a character such as a letter, number or symbol.
Camera format Video cameras CCD chips format; 2/3", 1/3", 1/4", etc. Camera Sensor: Video image sensor. CCD or C-MOS chip.
C-/CS-Mount Lenses and Cameras- The security industry has agreed upon a standard size lens mounting thread and coupling diameter with C and CS mount lenses. Cameras built with this type of lens mount can easily be configured with any of a large variety of C and CS mount lenses available for CCTV. Although C and CS are not exactly the same size, most cameras designed for this type of lens can accept either configuration using a simple plastic adapter. These lenses are standardized and will always thread properly, but exchanging C and CS mount lenses does require back focusing. This process requires the user / installer to slowly find the exact right thread position of the lens to ensure a clear video image. An industry standard for lens mounting. C-Mount is 1-inch diameter with 32 threads per inch. A C-Mount lens needs a C-ring when it is mounted on a CS-Mount camera. The C mount lens has a flange back distance of 17.5mm. The CS mount lens has a flange back distance of 12.5mm. C mount lenses therefore have a longer focal distance. CS mount became widely used, because it its more practical for many of todays more compact cameras. Lenses are often supplied with a 5mm spacer ring (sometimes called a C ring) that allows a C mount lens to be used on a CS camera. Most modern cameras are CS.
CCD stands for charged coupled device. This is a solid-state semiconductor element which uses hundreds of thousands of tiny pixel elements to accept light and translate that information into a vivid, visible picture image. A CCD is one type of camera image sensor. CCDs produce MUCH higher tvres, lower light sensitivity, and better overall video quality than CMOS imagers (also commonly found in CCTV industry cameras). One of the two main types of image sensing device used in cameras. It operates by converting light energy into electrical charge.
CCIR is the standard monochrome video format used in most of Europe, Israel, and some other places in the world. CCIR products are also generally referred to as PAL because all PAL products can also handle black and white CCIR video. Some camera models available on atss.in are also available in PAL / CCIR video format for foreign clients and special applications.
CCTMA Closed Circuit Television Manufacturers Association.
CCTV stands for closed circuit television: a video system which will only be monitored in a closed environment (as opposed to public broadcast). The realm of video security and surveillance is also referred to as CCTV. CCTV Is a Television system that sends a signal to one or more monitors rather than broadcasting over a public network, hence closed-circuit. A standard CCTV system will normally include a CCTV camera (for capturing video), transmitters and receivers (to transfer the video from the source to where it is recorded), a recording system (for video playback), and a monitor (for video monitoring). CCTV systems are primarily used for security purposes inside and outside buildings. However, they can also be used for specialist applications such as mobile police use and interrogation.
Chrominance refers to the part of the video signal that contains the colour information.
CMOS stands for charged metal oxide semiconductor. This is one type of camera image sensor which uses a charged metal surface to detect light and create a video image. CMOS technology is often smaller than CCD chips are currently capable of, so these cameras can often be quite miniature. While very low quality CMOS cameras are available for as little as $10 or $20, even the highest tvres CMOS cameras cannot compete with newer CCD imagers in the important fields of tvres, sharpness, and low light performance.
Coaxial Cable is the most common type of cable used for transmitting a video signal through copper wire. This type of wiring has a coaxial cross-section where an outer shielding protects the actual interior signal conductor from electromagnetic interference. In the CCTV industry, the term "coax" usually refers to RG-59 cable with BNC-type plug ends.
Codec refers to an internal computer component which processes analog information (like a video or audio signal) into a digital format such as MJPEG, MPEG-4, Wavelet, etc. for electronic storage on digital recording media. Without a codec in place to compress and digitize video, digital video recording to a hard disk drive would not be possible.
Color Camera - Cameras are available with either color or monochrome image sensors. Color cameras produce video images bearing the entire visible spectrum of colors. And because color CCD cameras have come a long way in recent years, the colors of objects appear vivid, crisp, and distinguished on monitoring and playback of video. The color cameras deliver amazingly crisp video, and in many cases better than the human eye when only a small amount of light is available.
Colour Saturation the degree of mixture of a colour and white. High saturation means little or no white.
Composite Video is the standard type of analog video signal utilized by most CCTV video cameras. This signal is plug and play compatible with most consumer television and VCR equipment. However, this type of video should not be confused with digital "component" inputs which may ALSO found on newer televisions and other home video equipment. A composite video signal has the correct phase rate, luminance, and chrominance information to be compatible with a particular video format such as NTSC, PAL, EIA, CCIR, etc. A full video signal that combines picture signal and synchronisation pulses.
Compression Digital video pictures can be compressed with a number of techniques. These include: JPEG and JPEG-2000 (for still images), M-JPEG and MPEG (for moving pictures).
Compression Method refers to the computer software technique the codec in a DVR video recorder (or DVR card) uses to convert the video signal to digital information so it can be compressed and stored on digital media like a hard disk drive, DVD, or CD. Uncompressed video would require massive processing power and nearly unlimited storage capacity and is, therefore, completely out of the question in the real world. MPEG (M-JPEG) and Wavelet are the most common types of compressed digital video, but there are variants of these in addition to other proprietary formats. MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 typically offer the highest quality recording (DVDs use MPEG-2), but smaller file sizes can be obtained by using a lower tvres, more efficient compression method like Wavelet or MPEG-4. It should also be noted that the method of compression a video codec uses to compress and digitize video information may NOT always indicate the video file type / extension for playback. Instead, the final digital video format available from a DVR recorder on backup (via USB, CD or DVD burner, etc.) could be in AVI format or even a proprietary format despite MPEG compression.
Contrast The noticeable difference between blacks and whites in a picture. If the two extremes look like gray and off-white the contrast is not good. A gray scale can be used to check the CCTV monitors ability to reproduce good contrast.
Contrast Control is a feature of many video monitors. This allows the user to manually adjust the screen contrast for better picture visibility.
Contrast Ratio is a monitor specification. This number indicates the dynamic range of brightness (difference between darkest and brightest) a monitor is capable of displaying.
CRT Cathode Ray Tube. The vacuum tube part of a monitor or television.
Current Delivery indicates the amount of electrical current (usually measured in milliamps, amps, or watts) available from some device which has output voltage (like an AC/DC power transformer or a battery pack). Current delivery describes the amount of "juice" a power supply or other product which outputs voltage can deliver to another product in need of electrical power.
Current Draw indicates the amount of electrical current (measured typically in milliamps or amps) required to safely and effpixelsly power a device.
Decoder A device used to recover the component signals from an encoded source.
Decibel (db) is a logarithmic scale. In the context of CCTV it refers to voltage or signal strength. A 6db increase is equivalent to doubling the signal strength.
Depth of Field (also known as depth of focus) refers to the range of distance from the camera that is in good focus. The smaller the aperture of the lens, the longer the depth of field. However, less light coming into the lens, means that the image will be dimmer, so the camera needs to compensate by increasing the gain. For example, the best (longest) depth of field would be obtained on a bright, sunny day, with a very small aperture on the camera. In this case the imaging device still gets a reasonable amount of light, even with a small aperture. The worst (shortest) depth of field would be in a dark room, with a large aperture. To improve depth of field, the best approach is to increase the amount of light on the subject, or use a more sensitive camera.
Digital indicates information which is encoded into ones and zeros (binary code) by some computer processing element. Digital in this industry, however, can refer to several different things. Digital signal processing is a feature of all Eyespyvideo.com CCD cameras and many multiple camera processors. Digital video refers to digital recording of video using a DVR video recorder or DVR card.
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) is a level of image correction or enhancement which takes place within a device using a digital computer element. This digital element encodes the information into digital information for the highest level of detail and quality. Cameras with DSP imagers do not necessarily produce "digital video," but they do provide very crisp video images. Quads and multiplexers offering DSP do not necessarily produce "digital video" either, but they do deliver very high tvres and often other dynamic characteristics.
Digital Video (DV) refers to video which has been compressed into digital information for storage onto digital storage media like a hard disk drive, CD, or DVD. The quality of digital video will vary depending on factors such as the camera quality and compression method.
Digital Video Recorder (DVR) - This device is capable of accepting one or more video (and sometimes audio) input signals for recording onto digital storage media. A DVR is basically a computer specifically designed to gather and compress video into a digital video format for storage on a hard disk drive or other form of digital media. DVRs are quickly replacing VCR video recorders for security and surveillance purposes without the need for changing tapes. Key differences between DVR and VCR recorders come to available features. Advanced DVRs are capable of accepting multiple video and / audio inputs without the need for bulky and expensive multiplexers or video quads. As well, most DVRs offer built-in motion detection recording (without costly and conspicuous PIR motion sensors), and many can be remotely viewed and played back over the internet. Some models may easily be backed up onto external media for long term archival. These backup methods may include CDs, DVDs, flash media cards, or via USB to a computer or other storage device. Eyespyvideo.com offers several DVR models, all selected for their superior reliability, ease of use, quality of manufacture and variety of useful features. This is a device that records video signal digitally. Normally this is on a large hard drive in the machine. For this reason it is sometimes known as a hard disk recorder (HDR). Digital Video Recorder records video pictures digitally.
DIP Switches Dual Interface Poll switches usually allow you to change the configuration of a circuit board to suit your application.
Directional Antenna - An antenna for wireless equipment which sends or receives a propugated radio signal on the same axis as the corresponding antenna on the other end (with line-of-sight visibility between the two whenever possible). While omni-directional antennas are great for short range broadcasts because of their versatility, high gain directional antennas are recommended for most long range wireless video applications.
Distribution Amplifier A device that provides several isolated outputs from one looping or bridging input, and has a sufficiently high input burden and input-to-output isolation to prevent loading of the input source.
DSL Digital Subscriber Line. A technology for bringing higher-bandwidth information to homes and businesses over ordinary copper telephone lines.
Digital Versatile Disk (DVD) Sometimes called digital video disk. This is an optical disk the same size as a CD, used for storing data of various formats. Including video, audio and computer data.
Direct Drive (DD) Some auto iris lenses require a DC signal from the camera. These are known as direct drive lenses.
Distribution Amplifier is a device that accepts one video input and sends it out to 2 or more devices. This is often used in a situation where the signal needs to be split between a number of video monitors or recording devices. 2 or 3 devices can often (but not always) be driven just by splitting the signal with a "T" connector, but more than that, and invariably a distribution amplifier is required to give an acceptable signal quality.
Duplex An electronic device used to record and display camera images at the same time. A full-duplex DVR can record camera images while displaying images from a different camera at the same time.
DVR Card - A DVR card is a device for installation in a home PC computer which converts that PC into a DVR digital video recorder by gathering video and compressing it into digital information onto a computers hard disk drive. When all works well, this allows a home PC to record up to several surveillance cameras. However, due to reliability concerns and software glitches associated with Windows® as an operating system platform, using PCI cards to record video is not recommended. A home PC is designed to perform many operations at once, but relatively simple functions. Recording digital video requires enormous system resources like computer memory and processor attention. Complete DVR digital video recorders designed specifically to handle recorded video (and solely recorded video) offer the benefits of reliability, as well as simple setup and use, a computer card can never achieve.
Dwell Time The length of time a switcher displays one camera before sequencing to the next.
EIA is the standard monochrome video format used in North America, Japan, and some other places in the world. EIA products are also generally referred to as NTSC because nearly all NTSC products like televisions and VCRs can also handle black and white EIA video. Electronic Industries Association. American standard for B/W camera system.
Effpixels Pixels concerns the operation of a cameras CCD image sensor. A CCD is comprised of hundreds of thousands of tiny pixel elements which translate light to a visible video image. But effpixels pixels must be distinguished from total pixels. Of the total number of pixels contained on a CCD image chip, some are not used for video imaging whatsoever. The number of effpixels pixels indicates exactly how many of the pixels are actively at work to deliver video. A higher number of effpixels pixels tends to indicate a higher tvres camera, though this number may not always describe actual video quality in the important categories of sharpness, color saturation and vividness, as well as low light performance.
Electronic Shutter This feature automatically changes the speed at which light is captured in fields of video by the CCD image sensor. Automatic electronic shutter determines the amount of light available and helps deliver the best quality video by dynamically adjusting for the current lighting conditions by toning down light levels in very bright situations and boosting brightness in low lighting situations. Compensates for moderate light changes in indoor applications without the use of auto iris lenses.
ELC (Electronic Light Control) Compensates for moderate light changes in indoor applications without the use of auto iris lenses. Select this mode when a fixed iris lens or manual iris lens is used.
Electronic Iris (EI) is an electronic implementation of an auto iris. It uses electronics to simulate the effect of opening and closing the iris, by increasing or decreasing the effective shutter time of the camera.
Enclosed Board Camera (a.k.a. module camera) - This term refers to cameras with their electronic board circuitry enclosed or housed inside a protective metal or plastic casing. Enclosed board cameras are not as delicate as exposed board cameras (although all electronics should be handled carefully), but they are also slightly larger and heavier.
Ethernet/Modem indicates a network communication device for computer-type devices. Most DVR video recorders with standard built-in Ethernet LAN connection (with RJ-45 plug) to enable remote internet viewing and/or network operation. Please click here to read more in our DVR frequently asked questions. The most widely installed Local Area Network (LAN) technology. Specified in a standard IEEE802.3.10/100 BASE-T, the most commonly installed Ethernet system, provides transmission speed up to 100 megabits per second.
Exposed Board Camera - This term refers to cameras with electronic board circuitry left exposed on the cameras without a housing or enclosure. These cameras are considered delicate and must be used and handled gently, but are great for some limited applications (like unmanned / radio-controlled vehicles, OEM applications, or body worn video use) because of their slim profile and low weight. In order to provide some degree of protection, all exposed board camera models found on this site come standard with 3M heat shrink coating. For a better protected miniature camera, please consider an enclosed board model.
Evidence Quality Includes specifics such as DVR recordings set at a resolution rate so that faces, number plates etc. can be identified, and accurate time and date information displayed with each recording.
External Sync allows a piece of equipment to take its video synchronisation from another unit, so that it can align itself with the system as a whole.
F-number (f-stop): Optical or lens speed. Smaller f-number means faster lens.
Focal Length indicates the distance between the optical center of a lens and a video cameras image sensor device. For practical purposes, lens focal length refers to a cameras angle of view. Lenses with a higher focal length number have more narrow, telephoto fields of view. A very low number focal length indicates a very wide field of view. It should also be noted that different cameras (photographic cameras, different imager sizes in video cameras, etc.) will deliver different viewing angles with the same focal length lens.
The distance between the centre of a lens, or its secondary principal point and the imaging sensor. Lower lengths give a greater field of view and less magnification. Longer lengths give a narrower field of view and greater magnification. The table below gives an approximate value for the angle of the field of view for lenses of various focal lengths. 30˚ is considered to be a normal view, telephoto (longer) lenses have lower angles. Most CCTV cameras have one of the 3 sizes of imaging devices listed below, 1/4", 1/3" or 1/2". As you can see, this makes a big impact when choosing lenses.
|
Focal Length |
Imaging Device Size |
||
|
1/4" |
1/3" |
1/2" |
|
|
2.8 mm |
64˚ |
80˚ |
97˚ |
|
4.0 mm |
45˚ |
60˚ |
74˚ |
|
6.0 mm |
30˚ |
38˚ |
57˚ |
|
8.0 mm |
23˚ |
30˚ |
40˚ |
|
12.0 mm |
15˚ |
20˚ |
30˚ |
|
16.0 mm |
11˚ |
15˚ |
22˚ |
|
50.0 mm |
4˚ |
5˚ |
7˚ |
Field - Video is generally "phased" (speed of real time display) at a rate of 2 fields per one frame of video. This type of system is referred to as 2:1 interlace. Therefore, fields per second and frames per second do not mean the same thing (this is common misconception in multiple camera processors and DVR recording). The number of fields per second is always twice as high as the number of frames per second. One video frame is composed of two fields; one field consists of the odd numbered lines in the frame and the other field consists of the even numbered lines.
Field of View refers to the angle at which a camera is able to produce a visible image. This angle can be described in terms of diagonal, horizontal, or vertical degrees. A cameras field of view is determined by its lens configuration. Fixed lenses have set fields of view, while cameras with varifocal or power zoom lenses have adjustable fields of view. The width, height or diameter of a scene to be monitored. Usually determined by the focal length of a lens, the sensor format and the distance to the objects.
Fixed Lens - A fixed focus lens has one set focal length with a specific field of view which cannot be changed. Any camera without a varifocal or power zoom has a fixed focus lens. All cameras offered a Eyespyvideo.com with fixed lenses are focused to infinity. This means that although the user cannot manipulate the field of view, everything in the picture beyond a few inches will be clear and in focus. Objects simply get smaller as they move further away from the camera (unlike a camcorder which may be focused only on a small area with blurred vision of the video image in the foreground or background of that area).
Fiber-Optic Cable One of the video transmission ways, being used for a long distance transmission up to miles.
Flash Memory Or flash RAM (Random Access Memory). A type of constantly powered non-volatile memory that can be erased and reprogrammed in units of memory called blocks.
Flat Panel Antenna - An antenna for wireless with a flat antenna element contained inside a protective weatherproof housing. As a highly directional antenna, a flat panel is intended to send or receive a propugated radio signal on the same axis as the corresponding antenna on the other end (with line-of-sight visibility between the two whenever possible). While omni-directional antennas are great for short range broadcasts because of their versatility, high gain directional antennas are recommended for most long range wireless video applications.
Frame - a full frame of video is the combination of two image fields interlaced together. A frame is one basic screen capture taken by a camera. 30 frames are displayed in one second of realtime video for NTSC format. PAL format is phased at a rate of 25 frames per second for realtime.
Frames per Second (FPS) describes the number of full video frames displayed or recorded within one second. True real time video consists of 30 frames / sec. for NTSC format and 25 frames / sec. for PAL format. Be sure not to confuse frames per second with "fields per second" or "images per second". A complete frame of video is compiled of two separate images (or fields), so the number of fields in one second is always twice the number of frames per second.
FPS Display Rate (a.k.a. screen refresh rate) indicates the number of frames per second a VCR or DVR recorder will display on a monitor for simultaneous viewing. Please DO NOT CONFUSE this specification with FPS Record / Playback Rate. The rate at which each camera is displayed is often NOT the same as the number of frames per second the recorder captures for playback. Many DVR sellers flash "real-time display rate" or "30 frames / sec. display rate" but do not in fact offer realtime playback of recorded video.
FPS Record Rate describes exactly how many frames per second a video recorder can actually capture. Analog recorders like VCRs can easily record in realtime (30 frames / sec. for standard NTSC) or timelapse (fewer than 30 frames / sec. for NTSC). Many digital DVR recorders, however, cannot record actual realtime video. Many sellers try to mislead consumers by advertising FPS Display Rate instead of actual record rate. For most situations, recording rate is the spec to pay attention to. However, please note specifications for digital video equipment are not the only numbers to rely on. In fact, many DVR recorders outperform their specifications upon real world testing while other low quality units often record at a much slower rate than their specs claim.
Frequency is the number of competed cycles of an electronic signal that occur in a given length of time. Frequency is usually measured in cycles per second (Hertz, Hz). For most CCTV industry equipment, frequency is used to describe the RF radio frequency at which wireless equipment operates. Frequency can also be used to describe the cycles of electrical current for the signal system.
FTP File Transfer Protocol a way to exchange files between computers on the Internet.
Gain indicates any increase or decrease in the strength of an electrical signal, often a wireless RF radio frequency signal when considering external antenna equipment. Gain is typically measured in terms of decibels (dB) or a number of times of magnification.
GB Gigabyte.
Genlock a device that adjusts the frequency of internal sync to an external data.
GHz (gigahertz) is a measure of frequency. 1 GHz = 1000 MHz = 10,000 KHz = 100,000 Hz.
GUI Menu stands for graphical user interface menu. Products which feature GUI menus can be programmed with on-screen guides similar to a home television or VCR.
Gamma a numerical value used to express contrast levels in television pictures. A value of "1" indicates a linear characteristic. Less than "1" indicates a curve or less contrast levels represented by a softer looking picture. The standard for a CCTV camera is ".45" and for CCTV monitors is ".55".
Gamma Correction refers to the correction of linear response of a video camera image sensor in order to compensate for the monitor phosphor screen nonlinear response. Without gamma correction set to the inverse (exact opposite corresponding value) of the monitors gamma, a video camera would not be able to provide a complete video image for a unified display. Gamma correction is measured with the exponential value of the curve describing the non-linearity.
Geometric Distortion the warped look of objects in a television picture due to erratic scanning of the electron beam in the picture tube or vidicon tube. A circle may look egg shaped or a straight line look like a curve.
Ghost refers to a poor image, where the primary signals is weak, allowing a secondary signal to interfere with the picture.
Grade A Chipset - CCD imager chips come in a variety of image and manufacture qualities, but grade A / 1st grade chipsets are always best. These types of CCD chips are made by the finest manufacturers in Japan and are only found in the BEST surveillance cameras. Because of their cost, the newest level of grade A chips are a minority in todays marketplace. Also, older grade A chips do not usually compare to the newest revisions and models. We carry cameras built with only the highest quality, and latest grade A CCD imager chips to bring our clients the absolute best image quality at an affordable price.
Grey Scale a pattern of vertical bars with shades of grey starting with white and gradually getting darker grey until ending at black. The pattern is used to test the ability of a CCTV camera to reproduce true white, black and the varying steps of grey in-between.
Hard Disk Drive (HDD) is a magnetic media storage device for recording digital information (like that used by computers or digital DVR video recorders).
HDD Capacity indicates the amount of information which can be stored on hard disk drive. This figure is measured in bytes. 1 GB = 1016 MB = 1032256 KB = 1048772000 bytes.
HDD Speed indicates the speed at which a hard disk drive is capable of encoding information. While many DVR sellers only use inexpensive, slow generic HDD drives (typically 5400 RPM with no buffer in place), DVR recorders are only equipped with 7200 RPM hard disk drives with 8 MB buffers from trusted brand names like Seagate, Western Digital, and Maxtor.
Homing a term used to describe a type of automatic sequential switcher, which will stop sequencing and remain on a single CCTV camera input displayed on the monitor when a switch or button is depressed. This switcher has only one monitor output.
Housing Protective enclosure that a camera can be placed in to protect it from outside weather conditions.
Hue Corresponds to colors such as red, blue, etc.
Hz (hertz) is a measure of frequency (indicates cycles per second in an electronic or RF signal). 1 GHz = 1000 MHz = 10,000 KHz = 100,000 Hz.
H.264 is a standard for video compression. It is also known as MPEG-4 Part 10, or AVC (for Advanced Video Coding). It was written by the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) together with the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) as the product of a partnership effort known as the Joint Video Team (JVT). The ITU-T H.264 standard and the ISO/IEC MPEG-4 Part 10 standard (formally, ISO/IEC 14496-10) are jointly maintained so that they have identical technical content.
Hub As a network product, a hub may include a group of modem cards for dial-in users, a gateway card for connections to a Local Area Network (LAN), and a connection to a line.
H.264
The latest video compression standard, H.264, is expected to become the video standard of choice in the coming years. It has already been successfully introduced in electronic gadgets such as mobile phones and digital video players. For the video surveillance industry, H.264 offers new possibilities to reduce storage costs and to increase the overall efficiency. H.264 (sometimes referred to as MPEG-4 Part 10/AVC) is an open, licensed standard that supports the most efficient video compression techniques available today. Without compromising image quality, an H.264 encoder can reduce the size of a digital video file by more than 80% compared with the Motion JPEG format and as much as 50% more than with the traditional MPEG-4 Part 2 standard. It is the magnitude of these numbers that makes H.264 highly relevant for video surveillance applications.
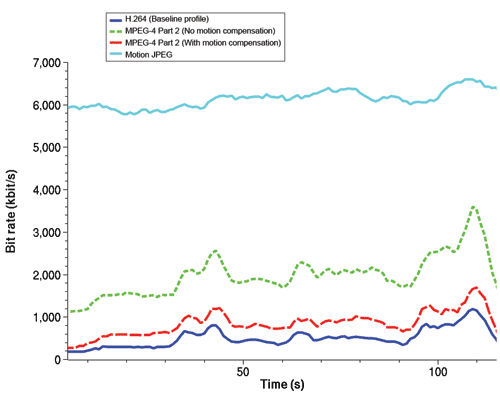
Bit rate comparison for a 115 seconds video stream, given the same level of image quality, among different video standards. The H.264 encoder was at least three times more efficient than an MPEG-4 encoder with no motion compensation and at least six times more efficient than Motion JPEG.
Reduced storage and bandwidth costs
One immediate benefit of the drastically reduced file sizes is the impact on storage and bandwidth requirements. For the same amount of video data, with the same image quality, a video surveillance system supporting H.264 compression will basically reduce the storage cost and bandwidth occupancy by at least 50% compared to when using conventional compression technologies. As the systems grow larger, and the requirements for high resolution images in combination with high frame rates increase, H.264 will be a key differentiator between various system solutions.
Higher resolution and frame rate
Depending on application needs, there are various ways to benefit from the impressive compression rate of H.264. Today, it is common to choose a limited frame rate or lower resolution in order to stay within the specified storage limitations of an application. This has a negative impact on the video images, which become either blurry or less detailed. Introducing video surveillance equipment that support H.264 compression in such an application will enable several combinations of increased frame rate and image resolution, thus providing higher image quality.
Accelerating use of megapixel cameras
H.264 is expected to accelerate the adoption of megapixel cameras within the surveillance industry. One of the current trade-offs of megapixel cameras is the large size of the recorded video data. As mentioned above, H.264 reduces the large file sizes without compromising image quality. It is likely that the highly efficient compression technology find the quickest traction in applications where there are demands for both high resolution and high frame rates, such as in the surveillance of airports, retail stores, banks and casinos.
Looking ahead
H.264 presents a huge step forward in video compression technology. With support from many industries and applications for consumer and professional needs – e.g. QuickTime, Flash, YouTube, iPod and Play- Station 3 – H.264 is expected to replace other compression standards and methods in use today. As the format becomes more broadly available in video surveillance equipment, system designers and integrators will need to make sure that the products and vendors they choose support this new open standard.
Origin of H.264
H.264 is the result of a joint project between the International Telecommunications Union’s Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG). ISO stands for International Organization for Standardization and IEC is an organization that oversees electronic and electrical standards. H.264 is the name used by ITU-T, while ISO/IEC has named it MPEG-4 Part 10/AVC since it is presented as a new part in its MPEG-4 suite. Jointly defined by standardization organizations in the telecommunications and IT industries, H.264 is expected to be more widely adopted than previous standards.
Hub As a network product, a hub may include a group of modem cards for dial-in users, a gateway card for connections to a Local Area Network (LAN), and a connection to a line.
Image Intensifier an electronic device which is used to amplify small amounts of light into usable amounts of light to produce a video picture.
Image Sensor indicates the type of semiconductor which handles video processing inside of a camera. Older CCTV cameras used tubes to process light information. CMOS and CCD image sensors are the most widely available for security cameras in todays market. CCD cameras provide by far the highest quality video of any type of image sensor.
Impedance the total opposition offered by a device to the flow of an alternating current. Measured in Ohms. CCTV industry has standardized 75-ohm impedance.
Incident Light the light that falls directly on an object.
Interference Extraneous energy which tends to interfere with the reception of the desired signals.
Interlacing PAL video signals transmit odd and even lines alternately. This is a 2:1 interlace. The two sets of lines are combined to form each single frame.
Interlaced Scanning a scanning process for reducing image flicker in which the distance from centre to centre of successively scanned lines is two or more times the nominal line width, and in which the adjacent lines belong to different fields.
Interline Transfer a technology of CCD design, where rows of pixels are output from the CCTV camera. The sensos active pixel area and storage register are both contained within the active image area. Differs from frame transfer where all active pixels are moved to a storage register outside of the active area.
Internal Sync Devices with internal sync, have an internal crystal to provide sync pulses, without needing reference from any external device.
INT Internal sync mode that sets to internal 2:1 interlace.
Input Voltage indicates the type of electrical current (AC or DC) and the voltage required to safely and effpixelsly power a device.
IP: Internet Protocol a set of rules to send and receive messages at the Internet address level.
IPCCTV Internet Protocol Closed Circuit Television
IP Waterproof Rating (IP66 - IP68) IP ratings are a BSi standard measurement for how waterproof something is. Many cameras or camera housings are designed for outdoor use, and therefore need to be waterproof to some degree. The details of the tests are defined in BS EN 60529 : 1992. The IP number has two digits, and optional letters after them. These have the following meaning:
|
Code |
Description |
|
First Digit |
Protection against ingress of foreign objects: · 0 means non-protected · 1 means Protected against solid objects over 50mm diameter · 2 means Protected against solid object over 12mm diameter · 3 means Protected against solid object over 2.5mm diameter · 4 means Protected against solid object over 1mm diameter · 5 means Protected against dust (Ingress of dust is not totally prevented) · 6 means dust tight and protects against access with a wire. |
|
Second Digit |
Protection against ingress of water: · 0 means non-protected · 1 means Protected against solid objects over 50mm diameter · 2 means Protected against direct sprays at an angle up to 15° from vertical · 3 means Protected against direct sprays at an angle up to 60° from vertical · 4 means Protected against direct sprays from all directions- limited ingress permitted · 5 means Protected against low pressure jets from all direction- limited ingress permitted · 6 means Protected against strong jets from all directions- limited ingress permitted · 7 means Protected against effects of immersion from 15cm - 1m, duration of test 30 minutes · 8 means protects against continuous immersion in water. |
|
First Additional Letter |
· A means protects against access with back of hand. · B means protects against access with finger. · C means protects against access with tool. · D means protects against access with wire. |
|
Supplementary Letters |
See BS EN 60529 |
E.g.,
IP66 - Total protected against dust and strong jets from all directions.
IP68 - Total protected against dust and long periods of immersion under pressure.
For further information or to get a copy of the standard, see the BSi website at www.bsi-global.com or www.bsi.org.uk
IR Infrared Light is a frequency of light which is lower than the human eyes visible spectrum (in the range of 850 ~ 950 nanometers). Color cameras CANNOT use infrared light whatsoever. However, this special band of light CAN be detected by most any monochrome CCD camera. Therefore, a black and white video camera in combination with Infrared lighting can see in pitch dark conditions where the human eye is unable to distinguish anything. An Infrared light source appears just the same as any visible light source on a black and white camera image. Infrared lighting for monochrome cameras should in no way be confused with new FLIR (forward-looking Infrared) spotting scopes or cameras which produce a grainy, green-tinted picture and do not require additional Infrared lighting sources.
IR Infrared Wavelength indicates the specific frequency of light (measured in nM - nanometers) an Infrared illuminator emits.
IR Illumination Range indicates the effpixels range at which a monochrome CCD camera can utilize the Infrared light from an illuminator and create an image. Eyespyvideo.com offers several camera models with built-in Infrared illuminators capable of casting light more than 40 feet in front of the camera. 40+ feet is therefore the IR illumination range for those cameras. Just like visible lights, more intense Infrared lighting sources will provide a larger illumination area and range.
Iris This is a mechanical device that adjusts to vary the amount of light passing through the lens of a camera. An adjustable opto-mechanical aperture built into a camera that controls the amount of lights coming through the lens.
ISDN Integrated Service Digital Network. A set of standard for digital transmission over ordinary telephone copper wire.
For further information or to get a copy of the standard, see the BSi website at www.bsi-global.com or www.bsi.org.uk.
IR Infrared Light is a frequency of light which is lower than the human eyes visible spectrum (in the range of 850 ~ 950 nanometers). Color cameras CANNOT use infrared light whatsoever. However, this special band of light CAN be detected by most any monochrome CCD camera. Therefore, a black and white video camera in combination with Infrared lighting can see in pitch dark conditions where the human eye is unable to distinguish anything. An Infrared light source appears just the same as any visible light source on a black and white camera image. Infrared lighting for monochrome cameras should in no way be confused with new FLIR (forward-looking Infrared) spotting scopes or cameras which produce a grainy, green-tinted picture and do not require additional Infrared lighting sources.
IR Infrared Wavelength indicates the specific frequency of light (measured in nM - nanometers) an Infrared illuminator emits.
IR Illumination Range indicates the effpixels range at which a monochrome CCD camera can utilize the Infrared light from an illuminator and create an image. Eyespyvideo.com offers several camera models with built-in Infrared illuminators capable of casting light more than 40 feet in front of the camera. 40+ feet is therefore the IR illumination range for those cameras. Just like visible lights, more intense Infrared lighting sources will provide a larger illumination area and range.
Iris This is a mechanical device that adjusts to vary the amount of light passing through the lens of a camera. An adjustable opto-mechanical aperture built into a camera that controls the amount of lights coming through the lens.
ISDN Integrated Service Digital Network. A set of standard for digital transmission over ordinary telephone copper wire.
JPEG is a standard for coding/compression of still pictures. It is used in the CCTV systems to compress and store individual frames of video. JPEG was developed by the Joint Photographic Experts Group.
This is short for Joint Photographic Experts Group international – a good and very popular standard for still images that is supported by many modern programs. With JPEG, decompression and viewing can be done from standard Web browsers.
JPEG compression can be done at different user-defined compression levels, which determine how much an image is to be compressed. The compression level selected is directly related to the image quality requested.
Besides the compression level, the image itself also has an impact on the resulting compression ratio. For example, a white wall may produce a relatively small image file (and a higher compression ratio), while the same compression level applied on a very complex and patterned scene will produce a larger file size, with a lower compression ratio
JPEG2000
Another still image compression standard is JPEG2000, which was developed by the same group that also developed JPEG. Its main target is for use in medical applications and for still image photography. At low compression ratios, it performs similar to JPEG but at really high compression ratios it performs slightly better than JPEG. The downside is that support for JPEG2000 in Web browsers and image displaying and processing applications is still very limited.
KHz (kilohertz) is a measure of frequency. 1 GHz = 1000 MHz = 10,000 KHz = 100,000 Hz.
Lens - A lens is an optical device which bends light, focusing it on onto a image sensor to create a distinct, visible image. All video cameras (and still cameras) need lenses in order to obtain a clear picture. Lenses come in a variety of focal lengths. The focal length of a lens, in combination with the size of the imager, will determine its field of view.
LAN Local Area Network. A group of computers and associated devices that share a common communications line.
LED Light Emitting Diode.
Lens Mount The area where a lens is mounted. There are two types; C- or CS-Mount.
Lens Speed Optical speed, expressed by f-number. Smaller f-number means faster lens.
Lens Selection - Atss offers many lens choices, but they vary by camera. At the bottom of each cameras specifications, its optional lenses are listed. For lens exchangeable cameras, there are a wide variety of lenses to choose from. In order to take the confusion out of selecting a lens, please click here to view a lens chart for 1/3" CCD cameras. So long as the distance and video target area have been determined, this chart makes lens selection a breeze.
Line Amplifier This device takes a weak video signal as its input and outputs a new stronger version of the same signal. These are useful/necessary for transmitting video over very long cable runs. This is sometimes known as a video line corrector.
Line Fed Camera refers to the use of equipment that can provide power to the camera and take the video signal along the same cable. It normally involves placing an "encoder" unit at one end and a "decoder" unit at the other. These units effectively combine and then split the power from the video signal at either end of the cable run.
Looping refers to connecting an additional device in parallel with an existing video cable. For example, when driving a video recorder as well as a monitor from the same video signal, simply by Ting off the cable.
Line-of-sight (a.k.a. LOS) Range refers to the ideal broadcast range of wireless audio/video link (transmitter and receiver) systems. Line-of-sight means the range when there is a visible pathway between the transmitter antenna and the receiver antenna. As well, the line-of-sight specification indicates performance under absolute best conditions. Please be aware that just like home cordless telephones, TV reception, and cellular phone reception, wireless audio/video equipment can often be less than perfect! All wireless products are subject to limitations and vulnerabilities due to many potential variables.
LL Line Lock mode LUX Lumens per Square Meter; unit of illumination amount.
Linux is a computer operating system platform upon which the software for many high quality standalone / network DVR video recorders is based. Due to reliability concerns and software glitches associated with Windows® as an operating system platform, using a PC-based video recorder for security or surveillance purposes is never recommended. All DVRs found on Atss feature embedded operating system platforms built on Linux.
Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) This is a technology used for flat screen displays. Aside from being smaller and lighter, it also has the advantage of using less power than traditional cathode ray tube screens.
Low Light (or low lux) Sensitivity refers to a cameras performance under low lighting conditions. Although many camera distributors flash very low light "lux" numbers, these numbers often times have nothing to do with real world performance. Specifications offered by CCD manufacturers list the absolute lowest light level at which some pixels will be altered. However, a human being looking at that recorded video will never be able to distinguish anything under the lowest lighting conditions (near pitch black). Please understand that the latest Sony 1/3 " Ex-View and Super HAD CCD chip sets have the best low light performance of any such other CCTV cameras on the market today.
Lux is a measure of light in terms of candle power (measured in foot candles). Lux is often given as a technical specification for cameras to describe the lowest level of light required for the camera to produce any kind of an image. However, this number lists the absolute lowest level of light needed to move ANY of the image sensors pixels. Since humans cannot detect this change in the image or let alone make out a distinguishable picture, this manufacturer specification is often exaggerated and misleading. Although generally speaking a lower "lux" rating indicates performance in darker conditions, the number listed cannot give a real determination of real-world performance. Eyespyvideo.com CCD cameras have been selected with the best low light sensitivity available (regardless of what any specs may claim).
This is a measure of the amount of light striking a surface. i.e. the luminus flux density at a surface. One lux is one lumen per square metre. Cameras for use in good lighting conditions, or in daylight would normally be rated at 2 Lux or more. Cameras with a Lux rating of 0.2 Lux or less would be considered low-light cameras. It is not possible to get good colour definition in low light levels, so in general low light cameras are always monochrome. However, day/night cameras use electronics to switch from colour during the daytime, to monochrome during night or low light conditions. Many low light cameras are also infra-red sensitive, so that infra-red illumination can be used. Particularly useful in zero light conditions.
|
Approximate Lux |
Description of Situation |
|
< 0.001 |
Starlight - overcast night |
|
0.001 - 0.01 |
Starlight - clear night |
|
0.01 - 0.1 |
Overcast Night |
|
0.1 - 1 |
Moonlight |
|
1 - 100 |
Dusk / Twilight |
|
100 - 10,000 |
Overcast Day |
|
10,000 - 1,000,000 |
Bright Sunlight |
Luminance refers to the part of a video signal that carries the monochrome information. i.e. brightness information.
Matrix Switcher is a device that allows any of its camera inputs to be switched to one or more of its monitor outputs. The outputs can of course also be video recorders.
MB Megabyte Mbps Megabits per second. A measure of bandwidth.
Mechanical Focus refers to the process of manually setting the focus on a lens
Mini-DIN Multi-wire cable with Mini-DIN connectors at both ends. Usually has 4 inner wires.
Motion JPEG - Motion JPEG offers video as a sequence of JPEG images. Motion JPEG is the most commonly used standard in network video systems. A network camera, like a digital still picture camera, captures individual images and compresses them into JPEG format. The network camera can capture and compress, for example, 30 such individual images per second (30 fps – frames per second), and then make them available as a continuous flow of images over a network to a viewing station. At a frame rate of about 16 fps and above, the viewer perceives full motion video. We refer to this method as Motion JPEG. As each individual image is a complete JPEG compressed image, they all have the same guaranteed quality, determined by the compression level chosen for the network camera or video server.
MPEG is a standard used for coding and compression of moving images. It was developed by the Moving Pictures Experts Group in the late 1980s). It is now used widely for the compression of video images. MPEGs basic principle is to compare two compressed images to be transmitted over the network. The first compressed image is used as a reference frame, and only parts of the following images that differ from the reference image are sent. The network viewing station then reconstructs all images based on the reference image and the "difference data". Despite higher complexity, applying MPEG video compression leads to lower data volumes being transmitted across the network than is the case with Motion JPEG. This is illustrated below where only information about the differences in the second and third frames is transmitted.
MPEG-1 was released in 1993 and intended for storing digital video onto CDs. Therefore, most MPEG-1 encoders and decoders are designed for a target bit-rate of about 1.5Mbit/s at CIF resolution. For MPEG-1, the focus is on keeping the bit-rate relatively constant at the expense of a varying image quality, typically comparable to VHS video quality. The frame rate in MPEG-1 is locked at 25 (PAL)/30 (NTSC) fps.
MPEG-2 was approved in 1994 as a standard and was designed for high quality digital video (DVD), digital high-definition TV (HDTV), interactive storage media (ISM), digital broadcast video (DBV), and cable TV (CATV). The MPEG-2 project focused on extending the MPEG-1 compression technique to cover larger pictures and higher quality at the expense of a lower compression ratio and higher bit-rate. The frame rate is locked at 25 (PAL)/30 (NTSC) fps, just as in MPEG-1.
MPEG-4 is a major development from MPEG-2. There are many more tools in MPEG-4 to lower the bit-rate needed to achieve a certain image quality for a certain application or image scene. Furthermore, the frame rate is not locked at 25/30 fps. However, most of the tools used to lower the bit-rate are today only relevant for non real-time applications. This is because some of the new tools require so much processing power that the total time for encoding and decoding (i.e. the latency) makes them impractical for applications other than studio movie encoding, animated movie encoding, and the like. In fact, most of the tools in MPEG-4 that can be used in a real-time application are the same tools that are available in MPEG-1 and MPEG-2. The key consideration is to select a widely used video compression standard that ensures high image quality, such as Motion JPEG or MPEG-4.
MHz (megahertz) is a measure of frequency. 1 GHz = 1000 MHz = 10,000 KHz = 100,000 Hz.
Manual Iris Lens is a lens with a built-in method of manually adjusting lens aperture for the best video quality for a specific lighting condition. Iris control on such a lens is set by hand to a particular fixed aperture, allowing for the best possible (often better than auto-iris lenses) brightness and contrast for a specific camera angle / shot.
Maximum Recording Time indicates the longest continuous duration of time which could be recorded onto storage media using a VCR or DVR video recorder. Maximum recording time for ALL recorders will depend on the user setting for timelapse or realtime recording and the amount of storage media capacity. Maximum recording time for DVR recorders is also dependent on tvres settings as well as hard disk drive capacity. Maximum recording time for analog VCR recorders will depend on the size cassette tape, usually VHS, which is installed in the recorder.
Micro Board Lenses are standard lenses for many cameras. These types of lenses are visible (not easily hidden like a pinhole lens) and range in size from 14mm to 25mm in diameter. Because it is physically larger than a pinhole lens, a micro board lens is able to accept more available light to provide the lowest possible low light performance.
Milliamps (mA) is a measure of electrical current power consumption. 1 amp (A) = 1000 milliamps (mA).
Milliwatts (mW) is a measure of RF radio frequency energy output. This term is most commonly applied to the RF output power of wireless A/V transmitters. For these types of devices, a higher number of milliwatts of output power indicates a more powerful (and usually further broadcasting) transmitter.
Modulator refers to a device which is capable of transforming an analog video or audio signal (or other type of electrical signal) into an RF radio frequency for wired installations. Modulating video into RF allows for longer cable runs in hardwired surveillance systems. Modulators, often called wired transmitters, also require a demodulating piece of equipment to reconvert the RF signal into a typical analog audio / video signal for proper display on a television, monitor, video recorder, etc.
Monitor used to view video pictures. These devices do not normally have television RF frequency receivers. They normally have composite or component video inputs
Monitor Screen Size indicates the actual physical size of a monitors viewing screen. However, this measurement is often different than the actual part of the monitor which produces a picture. The monitor viewing size spec describes the size of the picture on a monitor.
Monitor Viewing Size indicates the size of a monitors actual visible picture.
MOS Metal-oxide Semiconductor. One of video image chips like CCD, but it produces lower quality video.
Motorised Lens A camera lens equipped with small electric motor that enables focusing lens, opening or closing the iris diaphragm, or changing the focal length.
Monochrome refers to video captured in one monotone color scheme. For practical purposes, monochrome is another word for black and white in the video surveillance camera industry. Black and White signal.
Multiplexer (mux) is a video switching device that accepts video input from multiple cameras and converts them to all display on one monitor and / or video recorder, similar to a quad video processor. However, a multiplexer is far more advanced than a simple quad processor. Video multiplexers use time division multiplexing, meaning that a full frame of video from each camera is recorded every few seconds. While multiplexed video does not achieve true realtime display or recording (there is a slight drag to the images on playback), multiplexers do offer the capability to change between a view of several cameras and a solid close-up view of only a single cameras view on playback of recorded video. When using multiple cameras, quads and multiplexers help to cut down on the amount of additional equipment needed for a dedicated surveillance system. However, DVR digital video recorders with multiple video inputs are quickly replacing quads and multiplexers. DVRs are now capable of doing what required a processor and VCR in the past (plus a whole lot more).
ND Filter a filter that attenuates light evenly over the visible light spectrum. It reduces the light entering a lens, thus forcing the iris to open to its maximum.
Noise Undesired signals that corrupt the original video signals and may reduce the image quality.
NTSC is the standard color video format used in North America, Japan, and some other places in the world. Black and white EIA video products are also generally referred to as NTSC because nearly all NTSC equipment can also handle black and white EIA video. National Television System Committee; formulates standards for American colour television system. NTSC system has 525 horizontal scan lines and 30 frames per second.
Network Camera This refers to a camera that is designed to record pictures and transmit them directly over a computer network or dialup internet connection. Network cameras normally do not have any analogue video outputs. The images are encoded directly in one of the standard compression techniques, such as JPEG or MPEG.
Network Operation is a feature of many DVR digital video recorders. This allows the user to connect the DVR system to another computer or computer network for dynamic recording control and playback on other computers. Network operation is also interconnected with remote viewing capability for record and playback features over the internet. However, most network operation features are complex and not intended for most novice users. Connecting a DVR recorder to a PC network may require additional hardware such as a WAN or LAN router in addition to some prior networking knowledge and experience.
Omni-Directional Antenna - An antenna for wireless equipment which sends or receives a propugated radio signal in all directions simultaneously. This differs greatly from a directional antenna which is only capable of sending or receiving information on the same axis as the corresponding antenna on the other end. Omni-directional antennas are great for short range broadcasts because of their versatility. However, high gain directional antennas are recommended for most long range wireless video applications.
Operating System (or OS) indicates the basic computer platform a DVR video recorder operates with. Because of their stability and reliability,ALL feature embedded operating systems like Linux. DVRs with these operating systems are considered much more stable and reliable for obtaining important video evidence than competing Windows®-based DVR systems.
Operating Temperature indicates the temperature at which a device can safely and effpixelsly work.
Output Voltage indicates the type of electrical current (AC or DC) and the voltage a device will emit to safely and effpixelsly power another device.
Pan refers to horizontal (side to side) dynamic motion of a camera. Any equipment capable of panning can rotate back and forth along a horizontal axis. Some equipment, indicated as "PTZ," has the ability to pan as well as tilt and zoom.
Pan/Tilt/Zoom (PTZ) indicates equipment with the ability to pan, tilt, and zoom, usually by remote user control. Much of PTZ equipment is completely integrated, meaning there is only one controller necessary to operate all three features.
PAL is the standard color video format used in most of Europe, Asia, Israel, and many other places in the world. Black and white CCIR products are also generally referred to as PAL because all PAL equipment can also handle black and white CCIR video. Some camera models are also available in PAL / CCIR video format for foreign clients and special applications.
Peak to Peak (P-P) refers to the measurement of voltage of a signal between the most negative and most positive points. The amplitude difference between the most positive and the most negative excursions of a signal.
PPP, Point-to-Point Protocol for communications between two computers using a serial interface.
PPPoE Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet. Presets The pre-positioning of pan, tilt and zoom cameras by the use of potentiometers in the moving parts of the camera head. These allow the control equipment to store and move to a set reference point when the controller dictates or when an alarm exists.
PIR Motion Sensor refers to a motion detector with passive infrared technology. These alarm sensors are often used with alarm/event VCR and DVR video recorders to trigger recording upon the detection of physical movement. However, PIR motion sensors are bulky and expensive. As advanced video motion detection software continues to improve, motion detectors are quickly being replaced with the built-in features of high quality DVR recorders.
Parabolic Dish Antenna - An antenna for wireless equipment in the shape of a round concave dish or grid panel (similar to a home satellite dish). As highly directional antennas, parabolic dishes send or receive a propugated radio signal on the same axis as the corresponding antenna on the other end (with line-of-sight visibility between the two whenever possible). While omni-directional antennas are great for short range broadcasts because of their versatility, high gain directional antennas are recommended for most long range wireless video applications.
Pinhole Camera indicates a video camera with a tiny pinhole lens built-in standard with the camera.
Pinhole Lens is one type of standard lens available for many video cameras. A pinhole lens is only 1/16th of one inch in diameter, so cameras with tiny pinhole lenses can easily be hidden for covert video surveillance applications. Cameras with this type of standard lens are typically referred to as pinhole cameras. Most of the pinhole lens cameras available on Eyespyvideo.com have a 3.7mm focal length to deliver a wide field of view.
Pixel - A cameras CCD image sensor consists of thousands of tiny sensor elements known as pixels. These sensors detect information about light and colors and translate that information into a viewable video image through digital signal processing. Of the total pixels on a CCD imager, some are constantly dormant while others are effpixels and actively work to create an image.
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network. Quad Splitter Combines up to 4 video inputs into one channel and displays them on one monitor screen split into 4.
Power Consumption refers to the amount of electrical current an electrical devices requires for operation, usually measured in amps (A) per hour (often seen in mA milliamps, 1 amp = 1000 milliamps). For example, a miniature video camera which draws 100 mA per hour will consume 1 ampere hour for every ten hours of continuous operation.
Power Input Plug indicates the proper size and proper polarity configuration for a devices input voltage.
Power Output Plug indicates the proper size and proper polarity configuration for a devices output voltage.
Power Zoom indicates the ability to adjust a cameras field of view by remote control. Power zoom may also be described as remote zoom.
Quad Processor is a video switching device that accepts video input from four cameras and converts them to all display on one monitor and / or video recorder. When using multiple cameras, quads and multiplexers help to cut down on the amount of additional equipment needed for a dedicated surveillance system. However, DVR digital video recorders with multiple video inputs are quickly replacing quads and multiplexers. DVRs are now capable of doing what required a processor and VCR in the past (plus a whole lot more).
Quality Differences there are literally hundreds of different cameras available in the CCTV industry which on the outside appear very similar or identical to those offered at Eyespyvideo.com. However, inside these cameras (the crucial part) are so many different image sensors, each with different levels of performance, that it becomes quite confusing to even the experienced camera shopper. Beyond inspecting technical specifications and even the advertised CCD manufacturer, it is also important to test for actual real world performance. We thoroughly examine each part we stock (as well as many others which do not make the cut) to ensure their high tvres and performance under a variety of conditions. Eyespyvideo.com is proud to carry only the finest quality CCTV surveillance equipment available on the market today.
RAM Random Access Memory. The place in a computer where the operating system, application programs, and data in current use are kept temporarily so that they can be quickly reached by the computers processor.
RCA is a common connector plug for standard consumer video and audio equipment. This type of connector plug may also be described as a "phono" plug. RCA jacks are found on all VCRs and televisions equipped to handle a composite video input. In most cases, RCA jacks are color coded yellow, white, and red. BNC plugs are easily adapted to standard consumer RCA connectors using a simple one-piece plug adapter. All products include the necessary adapters so that users can select either BNC or RCA connections to suit their individual requirements for immediate plug and play use.
RF Frequency is a term used to describe radio signals coming inbound to a receiver or outbound from a transmitter (usually wireless). Radio frequency is a term reserved for radio signals at a frequency of more than 150 Hz.
RF Input Plug indicates the connection interface between pieces of wireless equipment. In most cases, the RF input plug refers to the appropriate plug type for connecting an antenna to a wireless transmitter or receiver.
RF Output Plug indicates the connection interface between pieces of wireless equipment. In most cases, the RF output plug refers to the type of plug coming from a wireless antenna for connecting into the RF antenna input plug on a wireless transmitter or receiver.
RF Output Power indicates the effpixels "strength" of a wireless transmitters audio / video signal. Generally speaking, RF output power (in combination with RF frequency) has a huge effect on the range one can expect from a wireless transmitter. Transmitters with higher output power (operating on the same frequency) will in most cases deliver a longer distance wireless broadcast range. All wireless link transmitters have been selected to feature high RF output power for consistent long-range wireless performance. RF output power is typically measured in milliwatts (mW) or watts (W).
Realtime (or real time) refers to video recorded at the same speed as action occurs (so it may be played back at the speed of real time without drag). Realtime video is phased at 30 frames per second (60 fields per second) for NTSC video and 25 frames per second (50 fields per second) for PAL format equipment. Basically all VCR recorders record realtime video, but MOST digital DVR recorders do not. DVR systems capable of both displaying AND recording realtime video for seamless recording of important action.
Receiver can refer to two different devices for CCTV. Wired receivers are used to demodulate video for extended video runs of more than one hundred and fifty feet. These receivers convert a video signal (and potentially a power and / or audio signal) from an RF radio frequency signal into composite video for TV display and recording. A transmitter at the opposite end of the wiring first modulates that signal into the RF frequency before sending it to the receiver for decryption. Wireless receivers similarly demodulate video (and sometimes audio) from an RF radio frequency, but this signal is "beamed" from a transmitter through the air without wires. A wireless transmitter sends it video images back to this wireless receiver. 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5.8 GHz wireless transmitters broadcast to matching paired receivers tuned to the same frequencies. 434 MHz transmitters are made to broadcast to any "cable ready" television or home VCR on channel 59 of the CATV band (i.e. a standard television or VCR with built-in tuner serves as the wireless receiver). Because wireless equipment can be quirky (just like cell phone or TV reception), high quality and professional wireless receivers are recommended. The wireless receivers all use FM modulation (more consistent and reliable than AM) and high gain standard antennas to help ensure fewer breakups in crucial video than substandard wireless link systems.
Receiver Sensitivity indicates the sensitivity of a wireless receiver in picking up a good reliable signal from the matching wireless transmitter using the stock antenna. Sensitivity measurements of -75 dB and lower indicate very high gain potential for a wireless receiver.
Recording Media refers to the magnetic storage device used to store recorded video. For many analog recorders this is a tape cassette, but DVR recorders use HDD hard disk drives. CDs and DVDs can also be types of media used to record digital video.
Recording tvres refers to the maximum number of horizontal lines of tvres a VCR or DVR video recorder is capable of recording. Most consumer recorders do not detect nearly the number of lines of horizontal TV tvres high quality CCD cameras produce. However, using a high quality, high tvres video recorder can yield brilliantly sharp images on playback. VCR and DVR video recorders have been selected for the highest tvres recording available for CCTV equipment.
Remote Control is a device used to control the features of a piece of equipment without physically adjusting anything on the equipment. Some products feature a wired remote control. This allows a user to control many functions remotely, but this controller must be plugged directly into the device. Other products can be used with a wireless remote control. These types of controllers allow the user to adjust functions remotely. The information is "beamed" wirelessly to the device using an IR infrared signal from the controller.
Remote Playback is a feature of many DVR video recorders. This allows users to play back recorded video over the internet from virtually any computer in the world.
Remote Viewing is a feature of many DVR video recorders. This allows users to monitor CCTV cameras over the internet from virtually any computer in the world.
Remote Zoom indicates the ability to adjust a cameras field of view by remote control. Remote zoom may also be described as powered zoom.
Resolution (TV lines) refers to the maximum number of vertical lines / pixel elements (horizontal tvres) a video camera is capable of displaying on a monitor or registering with a video recording device. Horizontal tvres indicates the number of pixel elements placed horizontally across each scanning line of tvres (vertical tvres). Horizontal tvres varies based on the abilities of each different camera and each different monitor. Although the number of TV lines of horizontal tvres is generally considered a measure of a cameras level of detail and sharpness, this specification does not always indicate true end video quality.
Retained Image also called image burn. A change produced in or on the target which remains for a large number of frames after the removal of a previously stationary light image and which yields a spurious electrical signal corresponding to that light image.
RF (Radio Frequency) a frequency at which coherent electromagnetic radiation of energy is useful for communication purposes. Also, the entire range of such frequencies.
RG59/U Cable One of coaxial cables suitable for video transmission in CCTV system.
Roll This is a fault condition on a video signal which refers to loss of vertical synchronisation. It causes the picture to continuously move up or down
Router device on the Internet that determines the next network point to which a data should be forwarded
RS-232 Port A communication port with 15 pins.
Saturation In colour, the degree to which a colour is diluted with white light or is pure. The vividness of a colour, described by such terms as bright, deep, pastel, pale, etc. Saturation is directly related to the amplitude of the chrominance signal.
Scanning the movement of an electron beam from left to right and top to bottom over a target area used to produce a video signal and reproduce a visual image.
Sensitivity in television, a factor expressing the incident illumination upon a specified scene required to produce a specified picture signal at the output terminals of a television camera.
Sequential Switcher Video Switcher. A device that allows the video signals from multiple cameras to be displayed on a monitor, or recorded on a VCR one at a time in sequence.
Server A computer program that provides services to other computer programs in the same or other computers. Or, the computer that a server program runs.
Spot Filter a small filter placed in the center of one of the elements of a lens to increase the ability of a camera to pass light. These filters are "neutral density" type which do not affect the colour rendition of the lens.
Scanning System refers to the method in which video information is processed for display on a monitor is an interlaced system in which each frame of video is scanned in two fields on a horizontal line. This type of system is called 2:1 interlace video.
SECAM Sequential Couleur AMemorie, a colour television system used in France, Russia and other countries that do not use either the NTSC or PAL system. It has 625 horizontal scan lines and 25 frames per second.
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. TCP/IP used in sending and receiving e-mail.
Signal System refers to the basic electrical system frequency a video image is phased on. In the United States and many other places across the world, 60 Hz is the standard for most all types of AC and DC electrical devices (including video cameras and monitors). For this reason, standard NTSC video is phased at a frequency of 60 Hz. PAL format video, on the other hand, has a signal phased at a rate of 50 Hz.
Simplex, Duplex, and Triplex concern the operation of video recorders and multiple camera video processors like quads and multiplexers. Simplex, duplex, or triplex capability reveals the number of device capacities which can be used simultaneously. For instance, a simplex device is only capable of performing one type of task at a time, whether that be recording or playback. A duplex device can perform two simultaneous functions like record and configure the monitor display for a certain close-up view. Triplex devices are capable of three tasks at the same time (usually record, playback, and zoom or other display functions).
S/N (Signal-to-Noise) Ratio indicates the ratio of noise to actual total signal (in a video or audio signal generally speaking). The S/N number measures how much higher the signal level is to the level of background electronic noise, so a higher number means a clearer and crisper picture. Signal-to-noise ratio is expressed in decibels (dB).
Storage Temperature indicates the highest and lowest possible temperature at which a device can safely and effpixelsly be stored or shipped.
Square Board Camera - A square board design refers to a camera with a square shape using a board-style video imaging chip (rather than an inline bullet design). These cameras are usually called "board cameras," though they may have either an exposed board or an enclosed board.
S-Video Transmits luminance and colour portions separately, using multiple wires, thus avoiding the colour encoding process and its inevitable loss of picture quality.
SVHS (Super Video Home System): Super VHS; a higher quality extension of the VHS home videotape format. Switcher Sequential Switcher or Video
Switcher A device that allows the video signals from multiple cameras to be displayed on a monitor, or recorded on a VCR one at a time in sequence.
Sync the part of a video signal which synchronises the scanning of a monitor to the scanning of an image device. There are vertical sync pulses and horizontal sync pulses which are used to keep the timing or start time of the electron beam in proper synchronisation.
Tearing a term used to describe a picture condition in which groups of horizontal lines are displaced in an irregular manner.
Terminated Used when referring to the end point of a video signal.
Tvres (Scanning lines) refers to something quite a bit different than what is generally considered to be tvres. Video display on a monitor requires the image to be constantly shifting (scanning) in order to display in real time. For instance, NTSC format video is based on a 525 scanning lines operating at a frequency of 60 Hz (PAL format is 625 lines, 50 Hz) for transmission and display of video images. This is an interlaced system in which each frame is scanned in two fields of 262 lines, which is then combined to display a complete frame of video with 525 scan lines. Scan lines (also referred to as "vertical tvres") of video are equivalent for each different video format, but every device must comply with these standards. Horizontal tvres, on the other hand, indicates the number of pixel elements contained placed horizontally across these scanning lines. Horizontal tvres varies based on the abilities of each different camera and each different monitor.
TCP Transmission Control Protocol. A set of rules to exchange messages with other Internet points at the information packet level.
TCP / IP Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol. The basic communication language or protocol of the Internet.
Termination refers to a 75 Ohm terminator that is used to terminate each end of a video line.
Time / Date Generator Installed between a CCTV camera and a monitor, it generates the information of Date, Time and camera ID.
TFT Is a variant of Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) which uses Thin-Film Transistor (TFT) technology to improve their image quality. TFT LCDs are one type of active matrix LCD, though this is usually synonymous with them. They are used in both flat panel displays and projectors. In computing, TFT monitors are rapidly displacing competing CRT technology, and are commonly available in sizes from 30 to 77 cm (~12 to 30 inches). As of 2006, they have also made inroads on the television market. There is no, or minor effect on the eyes, if we use TFT-LCD monitors.
Time Lapse VCR A video recorder that can be set to record continuously over long period of time. This can be anything from two hours to 960 hours.
Total Pixels concerns the operation of a cameras CCD image sensor. This number measures the complete count of pixel elements on a cameras CCD image sensor. This number should not be confused with effpixels pixels, which can provide a more telling description of a cameras tvres.
Tilt refers to vertical motion of a camera. Any equipment capable of tilting can move up and down along a vertical axis. Some equipment, indicated as "PTZ," has the ability to tilt as well as pan and zoom.
Timelapse is a feature of most CCTV-industry VCR and DVR video recorders. Timelapse refers to recording one still video image (frame) at fewer than 30 frames per second. The speed of this recording can usually be adjusted. Timelapse video is therefore slower than realtime recording and has a drag when the video is played back. One advantage of timelapse recording is the ability to increase maximum recording time so longer periods of time can be captured on a video tape or digital hard disk drive media. However, a major disadvantage of timelapse recording is missing many frames of video and missing much of what happens during a given period of time. There is no way to recover these missed frames on playback. For the ultimate in surveillance, realtime video recorders deliver the most complete and accurate video information of what occurred.
Transmitter can refer to two different devices for CCTV. Wired transmitters (sometimes called modulators) are used to modulate video for extended video runs of more than one hundred and fifty feet. These transmitters convert a video signal (and potentially a power and / or audio signal) into an RF radio frequency signal. A receiver at the opposite end of the wiring demodulates that signal back into traditional composite video for compatibility with standard equipment. Wireless transmitters similarly modulate video (and sometimes audio) into an RF radio frequency, but this signal is "beamed" through the air without wires. A wireless transmitter sends it video images back to a wireless receiver. Eyespyvideo.com 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz, and 5.8 GHz wireless transmitters broadcast to matching paired receivers tuned to the same frequencies. 434 MHz transmitters are made to broadcast to any "cable ready" television or home VCR on channel 59 of the CATV band. Because wireless equipment can be quirky (just like cell phone or TV reception), high quality and professional wireless transmitters are recommended. The wireless transmitters ALL use FM modulation (more consistent and reliable than AM), high gain standard antennas, and very high RF output power to help ensure fewer breakups in crucial video than substandard wireless link systems.
Television Lines (TVL) is a measure of the resolution of a video device. Higher number is higher resolution. 380 TVL is considered medium resolution. 480 TVL or greater is considered high resolution
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) is a special type of power supply commonly found in the security industry. This power supply is used to back up the system for ten minutes or more in the event of a main power failure. The time duration of this available emergency power depends on the size of the UPS and the current power consumption of the equipment in use.
UHF signal Ultra High Frequency signal. In television it is defined to belong in the radio spectrum between 470 MHz and 850 MHz.
Unbalanced signal In CCTV, this refers to a type of video signal transmission through a coaxial cable. It is called unbalanced because the signal travels through the centre core and returns via an earthed condutor. One conductor is a fixed voltage ie earth and only the other moves. In a balanced line system neither conductor is referenced to earth.
Underscan Decreases raster size in both H and V so that all four edges of the picture are visible on the monitor.
UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply. These are power supplies used in the majority of high security systems, whose purpose is to back-up the system when the mains power fails. The duration of this depends on the size of the UPS, usually expressed in output VA (or kVA), and the hold up time expected from fully charged batteries. There are two common types, "off line" and "on line". Off line uses a switch to change from mains to battery operation, thus there can be a short break in the output. On Line UPSs are a type where the convertor is always working, hence there is no switch over break at the ouput.
UTP Unshielded Twisted Pair. A cable medium with one or more pairs of twisted insulated copper conductors bound in a single sheath, with no overall or individual screen. Now the most common method of bringing telephone signals and data to the desktop.
Varifocal Lens is one type of lens found on some of our cameras. This lens allows the user / installer to manually adjust the cameras field of view. Varifocal lenses can therefore be changed to provide wider viewing angles or narrower telephoto viewing angles. Because of their adjustability, varifocal lenses are great when a camera will serve more than one purpose or to ensure proper focus without first determining an exact fixed lens focal length. Varifocal lenses are also typically referred to as zoom lenses.
Variable bit rate Operation where the bit rate varies with time during the decoding of a compressed bit stream. Used in MPEG 1.
Vectorscope An instrument similar to an oscilloscope, that is used to check and/or align amplitude and phase of the three colour signals (RGB). It has a circular, rather than rectangular screen, to show the phase angles of the component colours.
Velocity of propagation Speed of signal transmission. In free space, electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light (C). In coaxial cables, this speed is reduced by the dielectric material. Commonly expressed as percentage of the speed in free space i.e. 0.8C which is 0.8 x 3x108.
Vertical interval The portion of the video signal that occurs between the end of one field and the beginning of the next. During this time, the electron beams in the monitors are turned off (invisible) so that they can return from the bottom of the screen to the top to begin another scan. It is a time period where information can be inserted such as teletext, K codes and telemetry.
Vertical interval switcher A sequential or matrix switcher that switches from one camera to another exactly in the vertical interval, thus producing roll-free switching. This is possible only if the various camera sources are synchronized.
Vertical retrace The return of the electron beam to the top of a television picture tube screen or a camera pickup device target at the completion of the field scan.
Vertical shift register The mechanism in CCD technology whereby charge is read out from the photosensors of an interline transfer or frame interline transfer sensor.
Vertical sync pulse (also field sync pulse) A portion of the vertical blanking interval which is made up of blanking level lines of video. Synchronizes vertical scan of television receiver to composite video signal. Starts each frame at same vertical position. In total the vertical interval is 20 line long (CCIR & PAL).
VGA Video Graphics Array
VHS is the most common standard size for VCR cassettes. For normal VHS tape cassettes, there are three generally available recording lengths: T-120, T-160, and T-200. The number indicates the number of minutes recording on the tape in a VCRs highest tvres and fastest recording speed. However, the number of minutes attainable from such a tape is variable depending on the features of the VCR video recorder. For instance, most home VCR units have "extended play" or "slow play" modes to capture more time on a single tape. Many security VCRs also feature extended realtime recording and / or timelapse recording options to help conserve tapes. Video recording format used most often in homes but also in CCTV. Its limitations include the speed of recording, the magnetic tapes used and the color separation technique. Most of the CCTV equipment, today, exceeds VHS resolution.
VHF Very High Frequency. A signal encompassing frequencies between 30 and 300 MHz. In television, VHF band I uses frequencies between 45 MHz and 67 MHz, and between 180 MHz and 215 MHz for Band III. Band II is reserved for FM radio from 88 MHz to 108 MHz.
Video bandwidth The difference between the lowest and the highest signal frequency that a specific video signal can reach. The greater the video bandwidth, the better the quality of the picture. A video recorder that can reproduce a very broad video bandwidth generates a very detailed, high quality picture on the screen. The accepted bandwidth in CCTV is 5.5MHz for a colour signal.
Video Input Type refers to the type of video a device will accept for display, recording, etc. Our equipment (just like the majority of consumer video equipment most clients have at home) is made for compatibility with composite video. For use with S-Video, RGB component video, VGA, or other specialized / digital video formats, an adapter or converter may be required.
Video Input Plug indicates the plug size and configuration used for a devices video input. The most common types of plugs for composite video are BNC, RCA, and 1/8" mini.
Video Motion Detection is a feature of all DVR digital video recorders found on our Dvr. This is an advanced software feature which can detect motion in a cameras field of view and begin recording based on this motion detection. This type of detection can in most cases be adjusted in sensitivity. As well, a user can select and deselect areas in each cameras view for motion detection function. Advanced video motion detection erases the need for bulky and expensive PIR motion sensors.
Video Output Type refers to the type of video a camera or other device will output for display, recording, etc. on another device. Our equipment (just like the majority of consumer video equipment most clients have at home) is made for compatibility with composite video. For use with S-Video, RGB component video, VGA, or other specialized / digital video formats, an adapter or converter may be required.
Video Output Plug indicates the plug size and configuration used for a devices video output. The most common types of plugs for composite video are BNC, RCA, and 1/8" mini.
Video Quality is of course always subjective. However, when most users describe high quality video they are referring to a sharp and clear video image without distortion. Because of the high quality components and superior manufacturing of products found on Atss, these video devices feature amazing video quality. Consumers need to be aware that there are many quality differences available in the CCTV video surveillance industry.
Video Server (Network Video Server) is a device that accepts inputs from CCTV cameras using the PAL, composite video signal. It digitises the signal and then transmits images via a network, dialup or GSM connection. Advanced video servers have built-in video motion detection, and can buffer images while they are being uploaded to a remote server, where they are recorded. CCTV safe offer an advanced Video Server with all these features and more.
Video Switcher or Sequential Switcher. A device that allows the video signals from multiple cameras to be displayed on a monitor, or recorded on a VCR one at a time in sequence.
Video Distribution Amplifier (VDA) A special amplifier for buffering the video signal so that it can be supplied to a number of items of equipment at the same time. Each output will need to be individually terminated at 75 Ohms.
Video gain The amplification factor through any piece of equipment. Many loopthrough items are passive, i.e.. no gain.
Video equalization corrector (video equalizer) A device that corrects for the high frequency losses and/or phase errors in the transmission of a video signal along long lengths of cable. Video framestore. A device that enables digital storage of one or more images for a "frozen" display on a video monitor.
Video in-line amplifier A device providing amplification of a video signal.
Video matrix switcher (VMS) A device for switching more than one camera, VCR, video printer and similar to more than one monitor, VCR, video printer and similar. Much more complex and more powerful than simple sequential video switchers.
Video monitor A device for converting a video signal into an image.
Video printer A device to produce a hard copy printout from a video signal. It may be either a monochrome (B/W) or colour printer. They come in different format sizes and often special paper and inks are needed. Many computers now can be fitted with a video capture card, which means the print can be produced using a normal computer printer.
Video signal An electrical signal containing all of the elements of the image produced by a camera or any other video source.
Video switcher A device for switching more than one camera to one or more monitors manually, automatically or upon receipt of an alarm condition.
Video wall A video wall is a large screen made up of several monitors placed close to one another, so when viewed from a distance, they form a single large video screen or wall.
VLF Very Low Frequency. Refers to the frequencies in the band between 10 and 30 kHz.
VMD Video Motion Detector. A detection device generating an alarm condition in response to a change in the video signal, usually motion, but it can also be change in light. Very difficult to set up for use externally but can be useful in carefully controlled situations. Modern VMD systems can learn the scene and ignore such things as tree and foliage movement.
VOD Video On Demand. A service that allows users to view whatever program they want whenever they want it with VCR-like control capability such as pause, fast forward and rewind
Voltage Requirements generally refers to the amount of input voltage required to safely and effpixelsly power an electronic device..
Watts (W) are used to measure electrical energy. In some cases, this measure RF radio frequency energy output. In this circumstance, "watts" is most commonly applied to the RF output power of wireless A/V transmitters. For these types of devices, a higher number of milliwatts of output power indicates a more powerful (and usually further broadcasting) transmitter. However, "watts" can also be used to measure electrical power consumption. In order to calculate watts, simply multiply the number of volts a device uses by the number of amps it consumes. 1 amp (A) = 1000 milliamps (mA).
Watch-dog timer The automatic reboot of a DVR system whenever a problem is detected.
Wavelets This is a compression technique used to give high compression without degrading the image quality.
WAN Wide Area Network.
Wavelet a mathematical function useful in digital signal processing and image compression. In the Internet communications, wavelet has been used to compress images to a greater extent than is generally possible with other methods such as JPEG or MPEG.
Web Camera (or Web Camera Server) A CCTV Camera with built-in web server computer.
Web Server the computer program (housed in a computer) that serves requested HTML pages or files.
Weatherproof equipment has been specifically designed for safe use in most outdoor weather conditions. However, weatherproof equipment should not be considered waterproof because it is never intended for submersion under water. At the same time, there may also be extreme weather conditions which even standard weatherproof video equipment cannot function properly. Heating or cooling fans are encouraged for these types of conditions. For questions regarding special outdoor conditions, safe operating temperature for a piece of equipment should be consulted.
White Balance Control (WBC) is a built-in automatic OR user-configurable feature of every video camera . This term refers an electronic process used to retain crisp, vivid color saturation in the truest possible hues. The technology balances the image colors against a light colored object in the cameras view.
Wireless Operation refers to "beaming" a video and / or audio signal through the air without wires from a transmitter element to a receiver element. However, wireless equipment DOES still have some wires. All electronic devices need a connection to a power source (input voltage) to function. At the same time, plugs and wires are also necessary to attach a wireless transmitter to a camera or microphone. There will also be wires required to plug the wireless receiver into a monitor or recording device.
Wireless Camera is a term used too frequently in the CCTV, and especially miniature camera, industry. Any product touted as a "wireless camera" is simply a camera integrated with a wireless transmitter. We offer professionally concealed disguised cameras with built-in wireless transmitters, but we do not offer any strictly "wireless cameras." The overwhelming majority of these types of cameras currently available offer only poor quality CMOS video imaging and / or very low range wireless equipment.
Text Block
Text block body.
Yagi Antenna - An antenna for wireless with a series of antenna elements placed along a metal rod. As a highly directional antenna, yagi antennas are intended to send or receive a propugated radio signal on the same axis as the corresponding antenna on the other end (with line-of-sight visibility between the two whenever possible). While omni-directional antennas are great for short range broadcasts because of their versatility, high gain directional antennas are recommended for most long range wireless video applications.
Zoom refers to an adjustable field of view. Cameras may have manual zoom with a Varifocal lens or remote zoom with a powered zoom lens. Some DVR video recorders also have the ability to change the monitoring field of view and zoom in or out on selected areas of a recorded video image.
Zero Lux Operation refers to video imaging in pitch black (0.0 lux) lighting conditions. Monochrome CCD cameras can use IR Infrared lighting to yield crisp and distinguishable video images when absolutely no visible light is available.
1/8" (3.5mm) Mini Plug is an audio / video connector plug for some monitors and recorders. Camcorders are especially likely to use this type of plug for audio / video input and audio / video output. 1/8" mini plugs carry composite signals just like BNC or RCA plugs. However, the mini plug is smaller and can carry both a video and an audio signal over a single connector.
12VDC Most board cameras, mini cameras and about one third of the professional cameras work with 12VDC, 100mA to 200mA for B/W cameras and 150mA to 300mA for color ones. These cameras usually have DC jacks to accept DC power plugs. You should be careful about the polarity (positive and negative) for this power source. 12VDC power can be supplied by AC Adapter or battery pack. You may even use a "power cord" plugged to the cigarette lighter in a car.
24VAC About two thirds of the professional cameras work with 24VAC, 20VA to 40VA. The cameras usually have screw type connections and you dont need to worry about the polarity. This power is usually supplied by AC Adapter and you need to prepare separate power cable for the connection. Unlike 12VDC, this power can be transmitted to a long distance up to 450ft and is proper for the cameras that are to be installed outdoor or when you dont have the power outlet near the camera.